Meet the Noun
         | *leksilOgh'io* | Vocabulary |
|
| Nouns |
        | *Ang'elos* | angel |
       | *aghOri* | boy |
       | *alepU* | fox |
       | *Andras* | man, husband |
       | *gh'agh'A* | grandmother, old lady |
       | *dhAsos* | forest |
       | *elAphi* | deer |
     | *zOo* | animal |
      | *kafEs* | coffee |
         | *korItsi* | girl |
       | *krEas* | meat |
     | *mEra* | day |
       | *nAphtis* | sailor |
       | *pedhI* | child,kid |
        | *papUs* | grandfather,old man |
       | *spIti* | house |
     | *khOra* | country |
 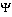     | *psarAs* | fisherman |
  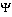    | *psAri* | fish |
|
| Other words |
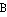      | *bhle-pi* | (he/she/it) sees, looks at |
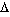   | *dhIo* | two |
     | *Ine* | (he/she/it) is, (they) are |
   | *Ena* | one (one) |
  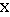     | *Erkh'ete* | (he/she/it) comes |
 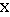   | *Ekh'i* | (he/she/it) has |
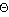  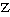 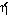    | *tha zIsi* | (he/she/it) will live, stay |
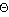        | *tha mIni* | (he/she/it) will stay, will live |
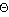            | *tha pandrephtI* | (he/she/it) will get married |
  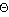  | *kAthe* | every |
   | *k'E* | and |
     | *kondA* | close, near (adv.) |
       | *lEgh'ete* | (he/she/it) is called |
    | *lEne* | (they) say |
  | *mE* | with |
    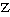   | *mn'Azi* | (he/she/it) resembles, looks like |
        | *mOnos tu* | alone, on his own |
    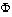  | *Omorphi* | beautiful (fem.) |
        | *pigh'Eni* | (he/she/it) goes |
     | *pIni* | (he/she/it) drinks |
     | *polA* | many (neu.) |
      | *polEs* | many (fem.) |
   | *sAn* | like |
  | *sE* | in, at, to |
       | *sIndoma* | soon, fast |
  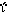 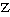   | *taIzi* | (he/she/it) feeds |
The fisherman
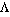






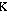




 .
. 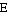




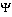



 .
. 









His name is Kostas. He is a fisherman. He has two children.













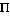



 ,
, 





























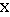



 .
.
The boy is called Pavlos, he is a sailor and goes to many countries.
















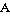















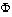










 .
.
The girl is called Anna and she is beautiful like an angel.
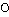
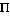




 ,
, 


 ,
, 



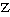



















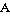















 .
.
Pavlos, they say, looks like his grandfather and Anna like her grandmother.
































 .
.
Kostas's house is close to a forest.















 :
: 














 .
.
The forest has many animals : foxes and deer.

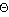




 ,
, 








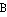







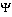







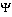








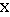








 .
.
Every day, a fox sees the fisherman's fish (plural) and comes near.
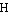

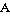








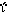
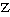






 .
. 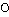
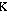












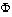










 .
.
Anna feeds her (with) meat. Kostas drinks coffee and looks at her.





















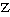
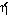















 .
.
Soon she will get married and she will live with her husband.
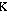



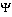


















 .
.
And the fisherman will stay on his own.
Grammar Notes
- This lesson presents the various forms of the noun. Noun is a word that refers to a person, animal or thing, action, state or property. Proper nouns are those that are used as names (e.g.,

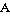





 ,
, 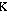




 ,
, 
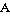


 ,
, 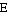



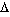
 ) and their first letter is always capitalized. Nouns in Greek are encountered in three genders (masculine, feminine and neuter), two numbers (singular and plural) and four cases. We will not say anything more about the genders and the number, since we encounter them in many other languages. The noun section describes how to identify the gender of a noun. In this lesson we will elaborate on the cases.
) and their first letter is always capitalized. Nouns in Greek are encountered in three genders (masculine, feminine and neuter), two numbers (singular and plural) and four cases. We will not say anything more about the genders and the number, since we encounter them in many other languages. The noun section describes how to identify the gender of a noun. In this lesson we will elaborate on the cases.
- The Nominative Case (
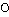








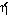




 ) is used whenever the noun is the subject of the sentence, i.e., the person committing the action described by the verb, for example,
) is used whenever the noun is the subject of the sentence, i.e., the person committing the action described by the verb, for example,


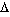





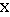

 (The forest has)
(The forest has)
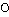
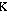









 (Kostas drinks)
(Kostas drinks)
or the subject of a reflexive verb, that is a verb whose action returns to the subject,
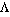






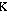




 (He is called Kostas)
(He is called Kostas)
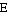




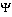



 (He is a fisherman)
(He is a fisherman)
In general, Nominative is the case that we use to answer to the question "



 ;" or "
;" or "
 ;" (="who?","what?")
;" (="who?","what?")
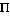




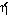

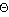
 ; (Who came?)
; (Who came?)
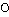

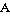





 . (Angelos (did).)
. (Angelos (did).)


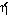

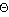





 ; (What came near?)
; (What came near?)
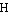





 . (The fox.)
. (The fox.)
- The Genitive Case (
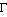




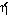




 ) is used to denote the owner of something. For example,
) is used to denote the owner of something. For example,










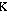



 (Kostas's house)
(Kostas's house)
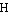










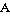



 (Anna's grandmother)
(Anna's grandmother)
It is the case we use to answer the question "





 " (or "
" (or "



 ") or "
") or "



 " (=whose).
" (=whose).
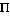













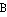

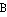


 ; (Whose is the book?)
; (Whose is the book?)



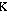



 ." ((It's) Kostas's.)
." ((It's) Kostas's.)
The Genitive is sometimes used to replace the preposition-article format, where the preposition is usually "
 ". For example,
This format has replaced the ancient Dative case (
". For example,
This format has replaced the ancient Dative case (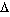




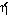




 ). There is also another use for Genitive. It is used to reveal/declare a property of the preceding noun, in the same way a noun is used in English as an adjective before another noun. For example,
). There is also another use for Genitive. It is used to reveal/declare a property of the preceding noun, in the same way a noun is used in English as an adjective before another noun. For example,
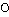











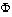





 = The oven potatoes (baked potatoes).
= The oven potatoes (baked potatoes).


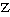





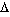




 = The forest animals.
= The forest animals.
This situation is not encountered in our text, but is useful to know for the subsequent lessons.
- The Accusative Case (
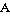







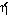




 ) is used for the object of the sentence, namely the recipient of the action described by the verb. For instance,
) is used for the object of the sentence, namely the recipient of the action described by the verb. For instance,

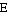
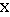







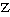

 . (It has many animals)
. (It has many animals)
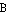









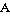


 . (He sees Anna)
. (He sees Anna)
It is used when answering the question "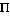



 ;" or "
;" or "
 ;" (="whom", "what") as in
;" (="whom", "what") as in
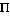




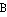





 ;. (Who(m) do you see?)
;. (Who(m) do you see?)




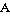




 . ((I see) Angelos.)
. ((I see) Angelos.)
- Finally, the Vocative Case (
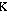





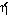


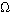

 ) is used whenever we call or address someone. E.g.,
) is used whenever we call or address someone. E.g.,

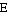



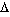
 ,
, 
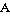




 ! (Come here, Angelos!)
! (Come here, Angelos!)
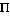




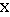
 ,
, 
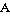


 ! (Look out, Anna!)
! (Look out, Anna!)
Remarks
- "
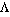





 " is a reflexive verb meaning "he/she/it is said/called". The expression "
" is a reflexive verb meaning "he/she/it is said/called". The expression "






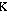




 " is another way to say "
" is another way to say "






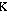



 " (="they call him Kostas). Note however that the case used in the first example is Nominative because "
" (="they call him Kostas). Note however that the case used in the first example is Nominative because "





 " is a reflexive verb, whereas in the second example Kostas is the object of the verb "
" is a reflexive verb, whereas in the second example Kostas is the object of the verb "


 " (="they call"), and as such it appears in the Accusative case. Keep in mind the following :
" (="they call"), and as such it appears in the Accusative case. Keep in mind the following :
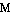






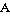




 =
= 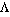







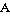





 = I am called called Angelos
= I am called called Angelos
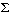






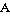


 =
= 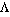







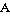


 = You are called Anna
= You are called Anna







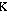



 =
= 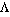






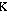




 = He is called Kostas
= He is called Kostas







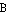


 =
= 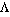






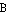


 = She is called Vana
= She is called Vana






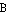




 =
= 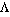






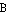




 = It is called Belgium
= It is called Belgium
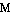







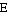





 =
= 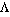









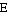





 = We are called Greeks
= We are called Greeks
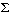






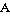









 =
= 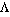






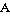








 = You are called Americans
= You are called Americans













 =
= 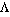












 = They are called men
= They are called men














 =
= 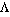














 = They are called women
= They are called women









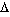

 =
= 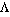










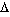

 = They are called children
= They are called children
You will understand this syntax better when we review the pronouns and verbs.
- There are some small words ("

 ", "
", "

 ", "
", "

 ", etc.) that look like the article but are actually short forms of the personal and the possessive pronouns. Thus
", etc.) that look like the article but are actually short forms of the personal and the possessive pronouns. Thus
- "

 " in "
" in "




 " stands for "it" ("They call it").
" stands for "it" ("They call it").
- The second "


 " in "
" in "











 " stands for "her" ("her grandmother's").
" stands for "her" ("her grandmother's").
- The second "


 " in "
" in "










 " stands for "his" ("his grandfather's").
" stands for "his" ("his grandfather's").
- "


 " in "
" in "




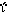
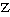

 " stands for "her" ("She feeds her").
" stands for "her" ("She feeds her").
- "


 " in "
" in "









 " stands for "her" ("Her husband").
" stands for "her" ("Her husband").
- "


 " in "
" in "






 " stands for "his" ("On his own").
" stands for "his" ("On his own").
- "

 " in "
" in "

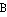




 " stands for "her" ("He looks at her").
" stands for "her" ("He looks at her").
Note that in the last example the final " " of the word "
" of the word "

 " is omitted because the next word starts with a consonant. More will be said about the short pronoun forms in the pronoun lessons.
" is omitted because the next word starts with a consonant. More will be said about the short pronoun forms in the pronoun lessons.
- Finally, note that the words "



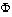

 " and "
" and "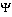



 " are in plural although their English translation ("deer", "fish") does not reveal it.
" are in plural although their English translation ("deer", "fish") does not reveal it.
 Main Page
Last modified: Sun Sep 22 13:12:22 1996
Main Page
Last modified: Sun Sep 22 13:12:22 1996


































































































































































































































































 Main Page
Last modified: Sun Sep 22 13:12:22 1996
Main Page
Last modified: Sun Sep 22 13:12:22 1996