A Brief Review of the History of Ancient Greek Philosophy | The Beginning | Socrates | Plato | Aristotle

Intellectuals were questioning the world around them as early as 6 th century BCE and the Ancient Greek philosophy can trace its roots to this time. Ancient Greek Philosophy was not interrupted throughout the Hellenistic period and well into the Roman period. The Ancient Greek philosophers studied a variety of subjects and not limited only to the philosophy of law and politics, ethics and aesthetics, metaphysics, ontology, logic, biology, rhetoric , etc. Proven Philosophers acknowledge today that Greek Philosophy highly influenced Western Civilization and Culture.
Socrates left his print on Ancient Greek Philosophy and is considered to have been the principle force for Ancient Greek Philosophy. Modern scholars have divided Ancient Greek Philosophy into three traditions:
- prior to Socrates or pre-Socratic Philosophy
- Classical Greek philosophy or the period during the empire of Alexander the Great
- and Hellenistic philosophy.
Pre-Socratic philosophy or the Athenian school was represented by Socrates, Plato and Aristotle . The Philosophers from this period concerned themselves with matters of cosmology, ontology and mathematics .
Milesian School was named after Thales of Miletus who, according to Aristotle, was the first philosopher. The Milesian School of Philosophy was later frequented by other well-known and famous scholars such as Anaximander and Anaximenes .

Xenophanes , a native to the region where the Milesian School was founded, may have been exposed to some of the Milesians’ cosmological theories and argued along the Milesian School’s principles. However, he differed profoundly from the Milesian School in that he was not a scientific man.
Pythagoreanism is a school of thought based on its founding member, Pythagoras . Pythagorean Philosophers confronted studied mathematics and the cosmos with the objective that they be in a musical harmony, while threading notions of ascetic ideals, purgation, metempsychosis, animal life into their work.
Heraclitus appears post Xenophanes and Pythagoras . His philosophy is based on the learnings that the entire cosmos is an ever-living fire (B30, The Fragments). According to Heraclitus, fire is a beginning principle of everything which changes into various other elements in the cosmic cycle. In other words, fire is λόγος and Zeus is like the thunderbolt that stirs all things. (B64, The Fragments).

Eleatic philosophy is named after Parmenides of Elea. Elea (Velia) was an ancient Greek city in southern Italy. He first argued that the first principle of being was One , indivisible , and unchanging . Another well known Philosopher from this period and School was Zeno of Elea who is known for his arguments, Zeno’s Paradoxes .
Pluralism and atomism were schools of thought marking Greek philosophy. Monism is based on the learning that one thing is the arche (ἀρχή). Such was the monism of the Milesians , Xenophanes, Heraclitus and Parmenides . Empedocles and Anaxagoras came to challenge this becoming known as the Pluralist Philosophers. They claimed that there were multiple elements. The Philosophy of Empedocles introduced love or strife and the Philosophy of Anaxagoras introduced the Mind. Ontological pluralism was introduced by Leucippus with respect to the cosmogony. He proposed two main elements, the atoms and the vacuum. Leucippus argued that the atoms having an inherent motion cross the void, thus, creating the real material bodies.
Sophistry is based on the juxtaposition of (φύσις-physis) nature or and law (νόμος-nomos). He proposed that nature was constant, while law and all things related to law could be changed. Protagoras is known to be the first among sophists, who claimed that “man is the measure of all things, of the things that are, they are, and of the things that are not, that they are not” (DK80b1). Plato reacted to this formulation by calling it "radical perspectivism." Other important sophists were Prodicus, Gorgias, Hippias and Thrasymachus.
Classical Greek philosophy is the golden era of Greek philosophy, because it marks a symbol for the life work of the greatest philosophers ever: Socrates, Plato and Aristotle.

Hellenistic philosophy represents a period of many different peoples co-existing. The philosophy of these peoples was shared during this societal change. Greeks, Romans, Egyptians, Syrians and Arabs became exposed to each other’s work, with strong Persian and Indian influences. There were 7 main schools during this period:
- Neoplatonism: Plotinus (Egyptian), Ammonius Saccas, Porphyry (Syrian), Zethos (Arab), Iamblichus (Syrian), Proclus;
- Academic Skepticism: Arcesilaus, Carneades, Cicero (Roman);
- Pyrrhonian Skepticism: Pyrrho, Sextus Empiricus;
- Cynicism: Antisthenes, Diogenes of Sinope, Crates of Thebes (taught Zeno of Citium, founder of Stoicism);
- Stoicism: Zeno of Citium, Cleanthes, Chrysippus, Crates of Mallus (brought Stoicism to Rome c. 170 BCE), Panaetius, Posidonius, Seneca (Roman), Epictetus (Greek/Roman), Marcus Aurelius (Roman);
- Epicureanism: Epicurus (Greek) and Lucretius (Roman);
- Eclecticism: Cicero (Roman).

The Hellenistic period is marked with the Roman Empire, which facilitated the spread of Christianity. Not only was Christian philosophy influenced by Ancient Greek Philosophy, but so was Jewish Philosophy and early Islamic Philosophy.
Middle Ages is a period of darkness for Western Europe. Losing contact with the Mediterranean world and the Middle East, ideas of Greek philosophy were forgotten by Western Europe, only to be re-introduced to them later through translation. Islamic philosophers translated Ancient Greek Philosophical works from Arabic into Latin. A lkindus, Alpharabius, Avicenna and Averroes re-interpreted many Ancient Greek philosophical works. The Philosophy of Thomas Aquinas is a product of their re-interpretations.
Music: Vangelis, "One morning at Pella" (Alexander The Great)
Artworks: Olivera Z. Mijuskovic, " The Ingenious Neuronal Pathways - Socrat, Plato, Aristotle" (The Guardian, London), "Fire of Heraclitus" (The Guardian, London), " Aristotle - eternal Mind" (The Guardian, London & the Holburne Museum, Bath, Somerset), "Arete of Cyrene - the beauty of Helens” , (The Guardian (London) the Holburne Museum, Bath, Somerset)
The Beginning
Nothing is more active than thought, for it travels over the universe, and nothing is stronger than necessity for all must submit to it. ~Thales
Ancient Greek philosophy contains not only philosophers from Greece but all philosophers who studied in ancient Greece and spoke and wrote in Greek/Hellenic. Ancient Greeks are the first people of the old century that knows itself as a free nation. It was not only political freedom , but the freedom of spirit that is embodied in the ancient Hellenic request: Γνώθι σαυτόν (Know thyself!) !
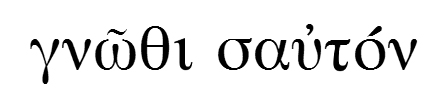

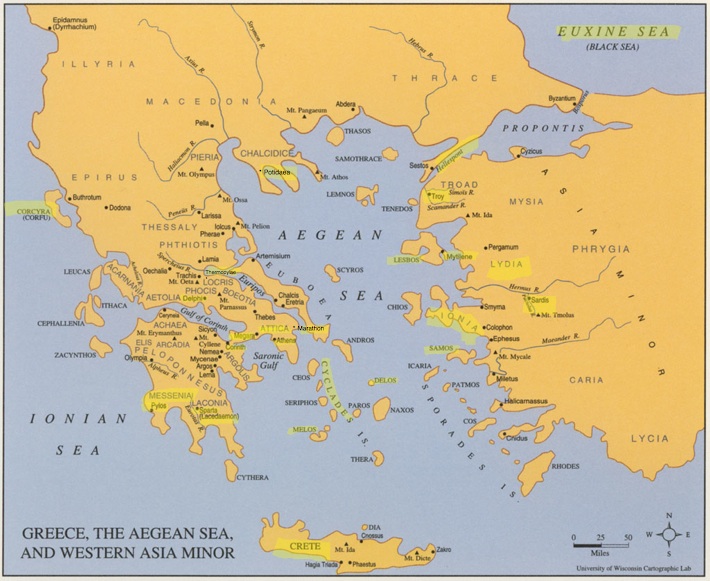
Thales lived in Asia Minor which was the Greek city-states bordered Persia. This area was known as Ionia. By opinion of many world wide scholars, Thales was first and only person from that period who claimed that natural phenomena were caused by forces of nature. People of this period believed that every natural phenomena were the work of Gods. It was understandable for the level of education and cultural development of that time.
Tales was a first man who is actually set up a scientific way of thinking not only philosophical.
He established the Ionian School of philosophy. This school was continued by his well-known student Anaximander . This school has influenced the famous teachings of philosophy that were later developed in Athens by Socrates and other very important philosophers.
Socrates

I know that I am intelligent, because I know that I know nothing.
Be slow to fall into friendship; but when thou art in, continue firm and constant.
Be as you wish to seem.
Socrates was born in Athens in the 5th century BCE. Athens was a center of education, culture and philosophy. Philosophers of that time including him were traveling from across Greece to teach rhetoric, astronomy, cosmology, geometry, and other stuff related to philosophy and science.
Socrates learned that all virtue is knowledge and that no one desires what is bad. If anyone does something that truly is bad, it must be consequence of unwillingly or ignorance.
Many of philosophical movements were inspired by Socrates and his younger associates. Socrates was the main interlocutor in Platos' dialogues. His most famous student was Aristotle. The philosophic movements dominate in the intellectual life of the Roman empire were following Socrates' activity directly or indirectly. Muslim world in the 7th through 10th centuries CE were influenced by Socrates' philosophy, also the West as foundations of Medieval philosophy and the Renaissance.

Plato

Human behavior flows from three main sources: desire, emotion, and knowledge.
A good decision is based on knowledge and not on numbers.
The greatest wealth is to live content with little.
Plato was born in Athens . He was younger than Socrates , more specific he was the generation after him.
There's evidence about his written work that claims about only 24 authentic dialogues. Many of modern authors believed that twenty-eight dialogues and just two letters were written by Plato but other thirty-six dialogues have a lot of defender. Socrates has the main role in his dialogues. Platos` political doctrine is explained in his: "The Republic" , "The Laws" and "The Statesman" . He learned that justice in the cities is only possible if the philosophers were kings.
Except about politics Plato spoke and about of metaphysics throw his learning about the theory of forms . He uses allegories in explanation of his ideas. The main allegory of him is the Allegory of the Cave . In this allegory he spoke about humans or most of humans tied up in a cave. That people look only at shadows on the walls and have no ideas about reality. If they turned around they would see what is actually the casting of the shadows. If they left that place they would see reality illuminated by the sun. When they from outside came back in cave they would tell others what they saw but no one believed. This allegoric speak about the view that philosopher-kings are wisest while most humans are most ignorant.

Aristotle

"Man is by nature a social animal; an individual who is unsocial naturally and not accidentally is either beneath our notice or more than human. Society is something that precedes the individual. Anyone who either cannot lead the common life or is so self-sufficient as not to need to, and therefore does not partake of society, is either a beast or a god."
― Politics
Aristotle was born in Stageira in Halkidiki . He moved to Athens in 367 BCE on studies of philosophy and rhetoric. There is a believing that he enrolled at Plato's Academy . About twenty years later left Athens because of his studies of botany and zoology. At the same time he became a tutor of one of the greatest emperors ever - Alexander the Great . After this period he returned to Athens to establish his own school: the Lyceum . His main work well-known as the corpus Aristotelicum cover a variety of subjects including logic, physics, optics, metaphysics, ethics, rhetoric, politics, poetry, botany, and zoology .
Aristotle wasn't very famous during the Hellenistic period because the logic of Stoa was very trendy. After this period authors of Peripatetic School back to life his philosophical work.